Theoretical Important notes for Memory Acquisition and Disk Encryption
- May 18, 2024
- 2 min read
Introduction:
In the world of digital forensics, thorough memory acquisition and disk encryption detection are essential steps in uncovering valuable evidence. This guide will walk you through the process of memory acquisition, tools used and the importance of considering disk encryption before proceeding with forensic analysis.
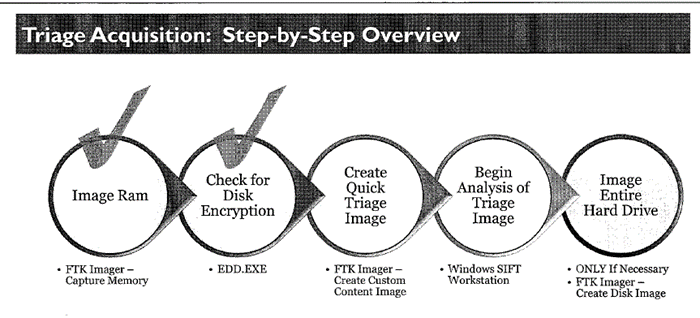
Step 1: Memory Acquisition For Live Systems:
Utilize tools like FTK Imager or USB tools such as MagnetForensics RamCapture, Belkasoft Live RAM Capturer, or DumpIT. For Dead Systems:
Capture hiberfil.sys (containing compressed RAM) and pagefil.sys, as well as MEMORY.DMP if available.
Tools like Kape and Redline can assist in memory acquisition, while WinPMEM and Volatility are invaluable for memory analysis.
Step 2: Checking for Disk Encryption
Consider Encryption: Assess the possibility of disk encryption before shutting down or removing a hard drive.
Use Encrypted Disk Detector (EDD): Scan local physical drives for encryption signatures, including TrueCrypt, PGP, Bitlocker, and more. https://www.magnetforensics.com/resources/encrypted-disk-detector/
EDD Functionality: EDD provides information about accessible encrypted volumes, aiding decision-making in incident response scenarios. Note:- that EDD does not scan for files within encrypted containers; its focus is on detecting mounted encrypted volumes.
Incident Response Use: EDD helps quickly identify encrypted volumes without intrusive actions, guiding the need for live acquisition.
EULA Acceptance: Users may need to accept an End User License Agreement (EULA) when using EDD; bypass this prompt by creating a shortcut with the "/accepteula" switch.
Step 3: Image RAM and Create Triage Image
Use FTK Imager to capture memory and create a triage image for initial analysis.
Step 4: Capture Essential Forensic Data
Collect critical artifacts such as $MFT, $Logfile, registry hives (SAM, SYSTEM, SOFTWARE, DEFAULT, NTUSER.DAT, USRCLASS.DAT), event logs (*.evtx), log files, .lnk files, .pf files, Pagefile.sys, Hiberfile.sys, RECENT folder contents, and the user's APPDATA folder.
(I have already created a complete guide of Collection of artifacts) (Please do check out under Resume tab in my website)
Conclusion:
Memory acquisition and disk encryption detection are fundamental steps in Windows forensics, enabling investigators to uncover valuable evidence and insights
Akash Patel

Comments